Synchronization maintains consistency in data values, regardless of where they are displayed.
Synchronization overview
Selecting a context selector or list item in a column or row on a grid card, synchronization updates any other pages and cards that display the selected data item. It's applied across cards, boards, worksheets, and hierarchies.
Global context
Global context refers to the synchronization of data in and across pages. This occurs by default, and means that a data item contains the same values wherever it displays in your app.
For example, say you choose the location USA on a context selector. If you open any other page from the same model containing the selector, you'll see the data for USA displayed in that location.
Synchronize across browser tabs
When working with pages in the same model across multiple browser windows or tabs, you can make sure data and context selectors automatically update in real time. Auto update supports up to five active tabs, and is switched off by default.
To synchronize data and context across browser tabs:
- Select Edit to open your page in designer mode.
- Select Edit selectors in the toolbar.
- Switch on the Sync data and context across tabs toggle.
- Select Publish.
Note: Your data will not synchronize across tabs from different browser types, or if you are using private browsing, such as incognito mode.
Context selector synchronization
Context selector synchronization refers to the synchronization that occurs by default between the elements on a page.
If a context selector on a card contains the same data item as a row or a column in a grid, selecting the row or column also updates the data displayed in the card.
When synchronization is disabled for a card, context selectors display in the card. In this case, the links are disabled between the card-level selectors and the page-level selectors.
Cards configured in this way are unresponsive to page-level selections. When a user chooses a different dimension on the card, the card value alone updates. No other items on the page are affected. Use this option if you want a published card to display the same values until an end user makes an alternative selection. For example, you could choose to display values for a list item, such as an individual user, when the page is opened.
You can display a context selector as a label in a card. This makes sure the value on the card isn't amended when the context is changed at page level. It also informs the end user which dimensions are selected for a card.
Users can select an item in a dimension in a card when they select its content. For example, you can select a grid row or a chart series. You can choose whether such context selections in a card change the page's context selection, or if the card maintains its own context.
When a card is synchronized with a worksheet, a selector or label chosen in the Card configuration panel won't display on the card. This is because the card uses the main grid selector that already displays in the Additional insights panel.
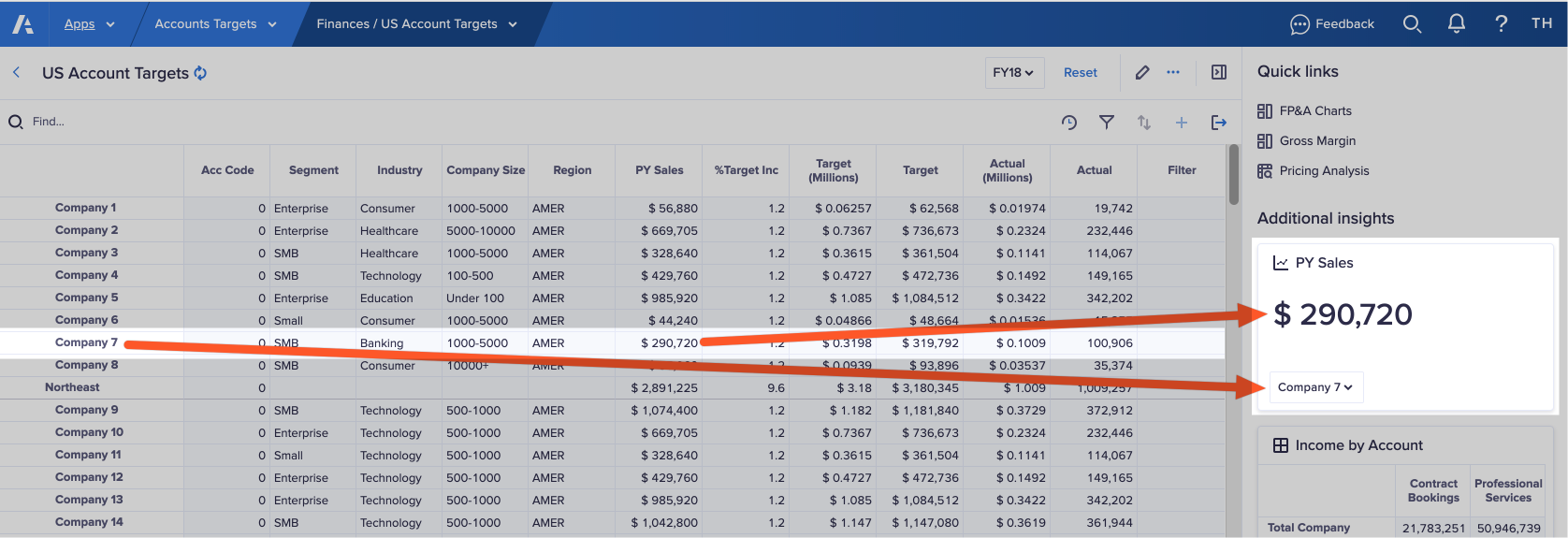
In the example below, a row heading is selected in a grid. The KPI card synchronizes with that selection and updates to display the value in the cell. The context selector also updates, as it contains the same data item, USA, as the row.
Hierarchy synchronization
Hierarchy synchronization refers to the synchronization of a:
- Main grid containing parent item values.
- Secondary grid containing child item values.
This is useful when, for example, a main grid contains a composite list, and you want to give end users the option to display its underlying data.
Composite lists are created by model builders from a series of lists, each of which is assigned a parent in the hierarchy. In a main grid, a user can choose a row or column, and the hierarchy filters display the child item values in the secondary grid.
A page builder can configure a hierarchy filter, which uses a common hierarchy to synchronize rows and columns across grids. Hierarchy filters enable end users to drill down to granular data in a second grid on a page. You can think of this second grid as a master detail grid.
For hierarchy synchronization to work, a page builder must enable the Rows and Columns hierarchy filters in the Card configuration panel for the second grid.

